What Is RAID in Project Management?
In project management, RAID refers to the identification and management of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies to help navigate obstacles and complete projects. Project managers use this framework to highlight potential challenges and dependencies, allowing for proactive decision-making.
What Does RAID Stand For in Project Management?
In project management, RAID stands for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. These four components provide a framework for identifying and managing potential challenges and dependencies in a project. Completing a RAID analysis helps ensure proactive responses and effective communication throughout the project lifecycle.
Here is a more in-depth look at the four components, along with an example of each from a human resources software implementation project:
| RAID Component | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| RAID Component Risk (R) | Definition These are uncertain events or conditions that, if they occur, can have an effect on the project outcome. | Example Resistance from employees might impact the adoption rate of the new HR software. |
| RAID Component Assumption (A) | Definition These are conditions believed to be true or things assumed to be in place, upon which the project plan is based. | Example All employees have the basic computer skills necessary to navigate and use the new HR software. |
| RAID Component Issue (I) | Definition These are current challenges or problems that are negatively affecting the project or have the potential to do so if not addressed. | Example There are technical glitches in the newly implemented HR system that need to be resolved |
| RAID Component Dependency (D) | Definition These are tasks, milestones, or components that are reliant on one another for their progression or completion. | Example The training schedule for the new HR software is dependent on the successful installation and setup of the software. |
How to Do a RAID Analysis
To do a RAID analysis, brainstorm and categorize potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies, then document, prioritize, and develop action plans for each. Perform regular monitoring, communication, and post-project reviews.
The earlier you begin your RAID analysis, the better. “Start early. Don’t wait for issues to become apparent. Initiate your RAID analysis during the project planning phase,” suggests Teresha Aird, Co-Founder and CMO at Offices.net.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting a RAID analysis:
- Define the Scope and Objective: Before starting, ensure the project’s objectives and scope are clear. This provides context for the RAID analysis. Learn more about defining project scope and objectives.
- Brainstorming Session: Gather the project team, stakeholders, and any relevant expert for a brainstorm. “Use brainstorming sessions to identify and document potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies related to the project,” says Percy Grunwald, a personal finance expert and Co-Founder of Compare Banks. Encourage open communication and ensure every voice is heard.
- Categorize: Identify your risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
- Document: Create a RAID log, a living document where you record each identified item. Update the log regularly. For each item, provide details such as description, impact, likelihood, mitigation strategies, and assigned responsibility. Choose from this collection of free RAID log templates to get started.
- Prioritize: Be sure to perform this step, especially for risks, and rank them based on likelihood and impact. This helps with focusing resources on the most significant challenges. For issues, determine their urgency and impact to prioritize their resolution. “By prioritizing in this way, it can guide your action plans going forward,” explains Aird.
- Develop Action Plans: For each risk, define mitigation or contingency plans, then clarify and validate assumptions, assign responsibility for resolving issues, and map out how dependencies affect the project timeline. Learn how to create an action plan and download a template.
- Monitor and Update: Regularly review the RAID log throughout the project lifecycle and update with new findings or as situations change. As risks materialize or issues are resolved, record the outcomes and lessons learned. “Regularly review and update the RAID log throughout the project's lifecycle, and communicate findings to all relevant team members to ensure proactive management of project-related challenges,” recommends Grunwald.
- Communicate: Keep stakeholders informed by sharing the RAID log or updates. Encourage team members to report any new risks, assumptions, issues, or dependencies they identify. “Involve key stakeholders and team members in the analysis to ensure a 360-degree perspective,” recommends Aird.
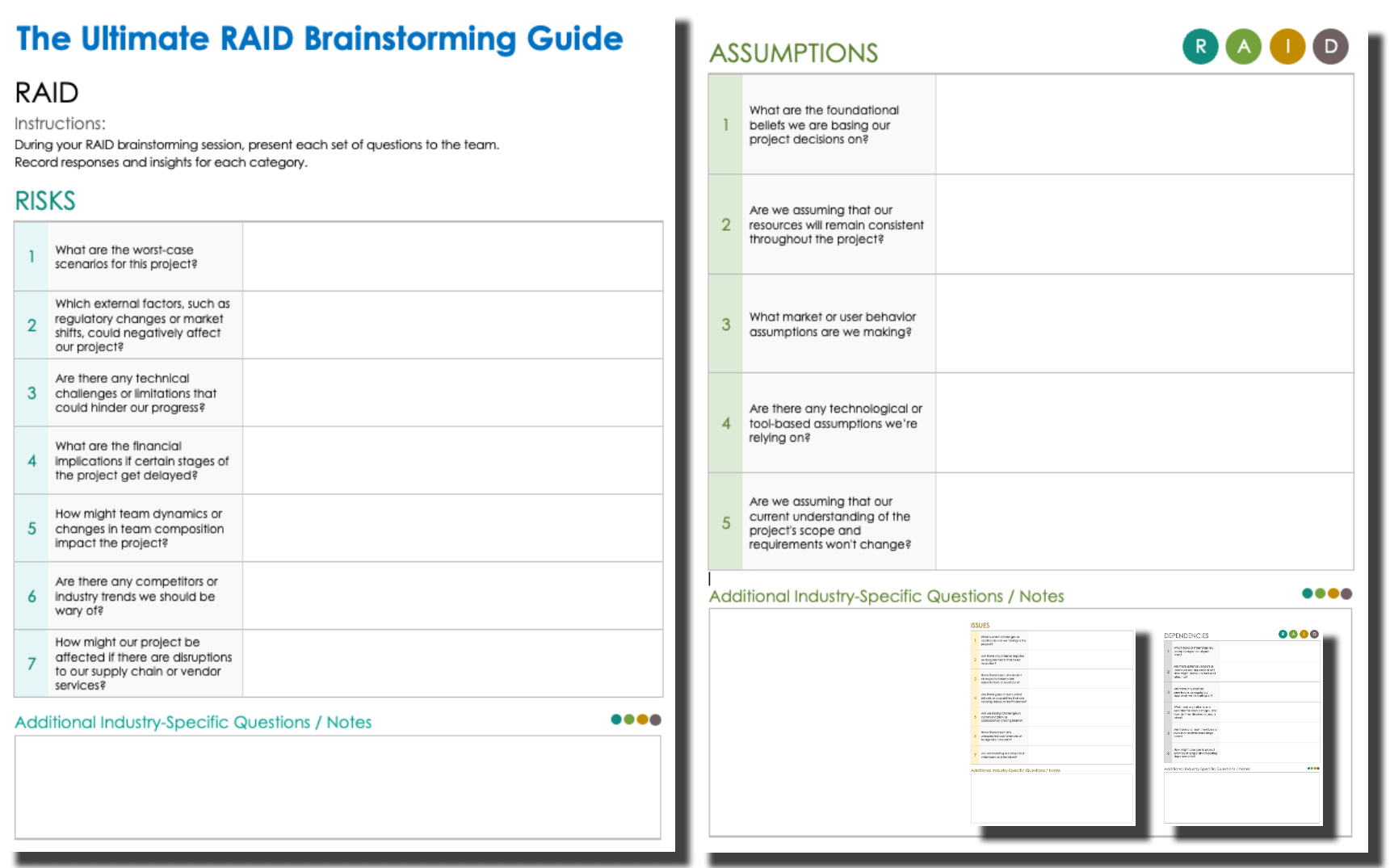
The Ultimate RAID Brainstorming Guide
Download the Ultimate RAID Brainstorming Guide for Microsoft Word
Download and print this brainstorming guide to bring to your next RAID brainstorming session. The guide includes foundational questions for identifying risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies for any project. The questions aim to be comprehensive, but they can be customized to suit the needs of your project. Simply go through each question as a group and record responses in the space provided. The template includes an area to enter industry-specific brainstorming questions.
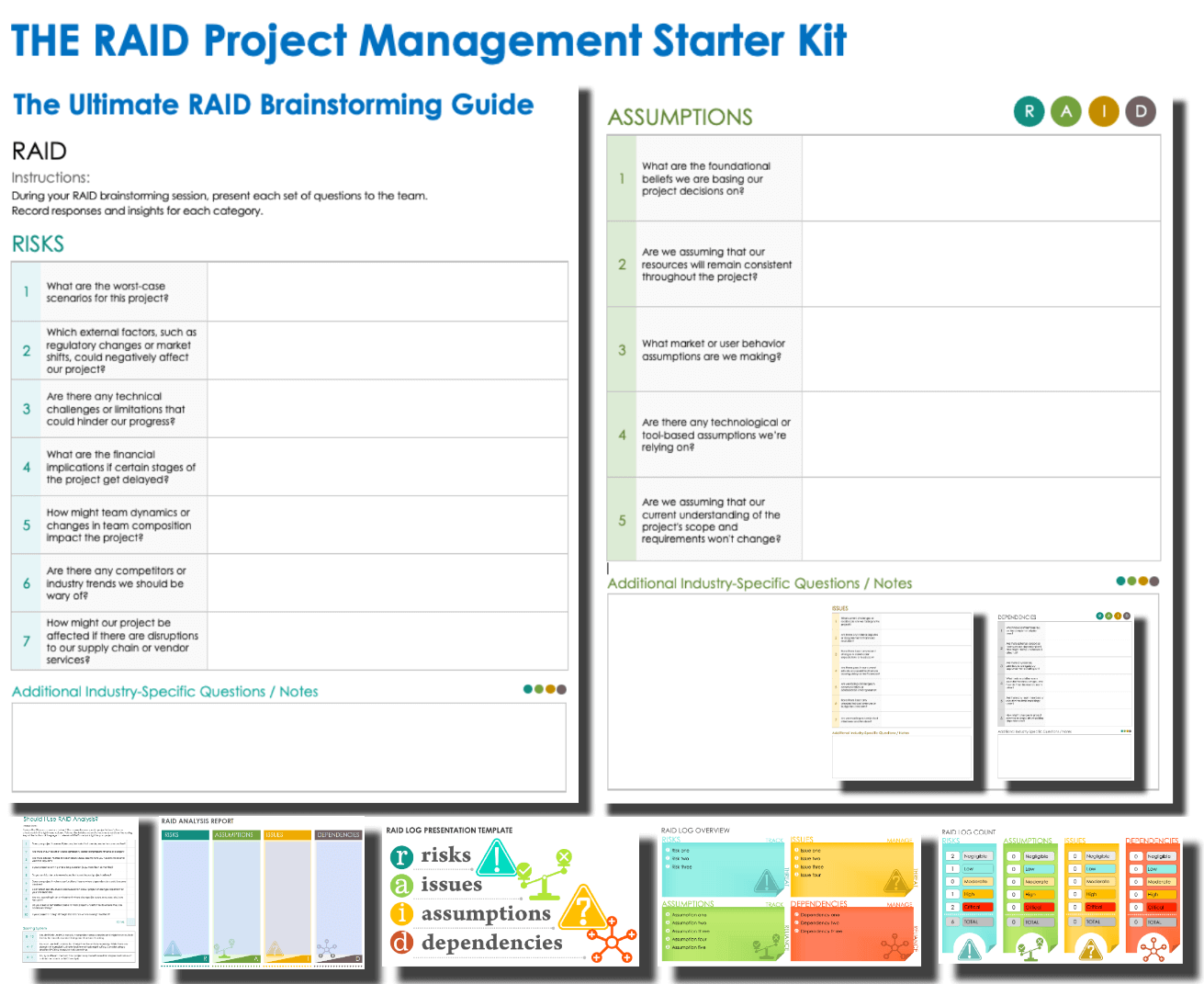
RAID for Project Management Starter Kit
This starter kit includes everything you need for effective RAID project management. Start with the kit’s RAID analysis quiz to ensure RAID management is right for your upcoming project. Then use the brainstorming guide to help your team identify important risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. Finally, use the several RAID analysis reports and RAID log templates to record and track the status of each component.
Download the RAID for Project Management Starter Kit
In this kit, you’ll find the following:
- The “should I use RAID analysis” quiz for Microsoft Word to help determine whether or not to use RAID for a specific project.
- A RAID brainstorming guide for Microsoft Word to bring to your brainstorming session.
- A RAID analysis report template for Microsoft Word , Adobe PDF , and Google Docs to help you perform a complete RAID analysis.
- A RAID log presentation template for PowerPoint and Google Slides to update stakeholders on the status of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
Examples of RAID in Project Management
By reviewing RAID analysis examples, project managers can gain insight in identifying and managing risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies in real-world scenarios. Use the following examples to refine your approach and avoid common pitfalls.
The following example is the result of a team brainstorming session where the team identified the RAID components for an upcoming project. This project involves the development and launch of a new project management software designed for remote teams.
Notice how this list spans a wide range of concerns, from technical challenges to market-based concerns, and balances internal and external assumptions. Each entry is detailed and specific, making it easy to understand and prioritize.
Below are additional, industry-specific examples of RAID analysis:
- Construction
- Risk: Delays due to weather conditions could push back the completion date.
- Assumption: The allotted land has been properly surveyed and is stable.
- Issue: There has been an unexpected discovery of underground utilities, which might require rerouting or design changes.
- Dependency: The commencement of electrical work is dependent on the completion of foundational structures.
- Healthcare and Medical Research
- Risk: A new drug being developed could have potential side effects, which might affect its approval.
- Assumption: Participants in a clinical trial adequately represent the broader population.
- Issue: The research time is having difficulty recruiting enough participants.
- Dependency: The final approval of a drug is dependent on successful outcomes in the initial trial phases.
- Event Management
- Risk: Low ticket sales for an upcoming concert could affect profitability.
- Assumption: Most attendees will prefer online registration methods over traditional ones.
- Issue: There are technical difficulties during a virtual event.
- Dependency: The start of an event hinges on completing sound checks on time.
- Software Development
- Risk: The discovery of code vulnerabilities could lead to security breaches.
- Assumption: Users will quickly adopt a new software update within the projected time frame.
- Issue: Bugs have been detected.
- Dependency: The progress of front-end work is contingent on the completion of back-end development.
What Is the Purpose of a RAID Analysis in Project Management?
The purpose of a RAID analysis in project management is to proactively identify, prioritize, and manage potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. By doing so, project teams can mitigate obstacles, resulting in more accurate planning, better stakeholder communication, and more.
By conducting a RAID analysis, project managers can do the following:
- Highlight Potential Challenges: By identifying risks and issues early, teams can develop mitigation strategies to address them before they escalate. Use a risk assessment template to plot out risks and create a risk management plan to figure out how to handle their impact before they occur.
- Clarify Assumptions: Recognizing what has been assumed helps in verifying those assumptions, reducing the chances of unexpected surprises.
- Identify Dependencies: Knowing what tasks or components are interdependent ensures that project scheduling and sequencing are accurate and realistic.
- Enhance Communication: By maintaining a RAID log, stakeholders can stay informed about potential challenges and the steps taken to address them, fostering trust and transparency.
- Make Informed Decisions: With a clearer view of uncertainties and dependencies, managers and teams can make decisions that are aligned with the project's objectives and constraints.
Overall, RAID analysis acts as a tool to ensure smoother project execution and to reduce the likelihood of unforeseen challenges derailing a project.
Why Is a RAID Analysis Important in Project Management?
A RAID analysis is important in project management because it enables teams to proactively address challenges, allocate resources effectively, and ensure smoother project execution. This structured approach enhances stakeholder communication, facilitates informed decision-making, and increases the likelihood of project success.
Project managers who incorporate RAID analysis into their plans are more adaptable leaders. “A RAID analysis serves as an early-warning system, allowing you to preempt challenges and allocate resources more effectively,” explains Aird. “It also promotes better communication among team members and stakeholders by ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding project vulnerabilities and contingencies.”
In his paper, “The Toolbox for Faster Projects and Awesome Products,” presented at PMI® Global Congress in 2007, Gregory D. Githins identifies RAID not only as a tool for improving project outcomes, but for enhancing an individual’s thinking process. He writes that the managerial tools such as RAID, “function to help a person think better by making the individual more conscious of his or her data and inferences.”
Advantages of RAID Analysis in Project Management
RAID analysis in project management leads to better decision-making and resource allocation. This structured approach enhances project transparency, fosters timely issue resolution, and boosts stakeholder confidence, ensuring projects align more effectively with broader company strategies.
Here are some advantages to conducting a RAID analysis in project management:
- Proactive Risk Management: By identifying potential risks early on, project teams can develop strategies to mitigate them. “A RAID analysis helps you foresee and plan for challenges, thus reducing fire-fighting later in the project,” explains Aird.
- Clearer Assumptions: By explicitly stating and documenting assumptions, the project team can verify and validate them. This reduces surprises and misalignments that arise from unchecked assumptions.
- Timely Issue Resolution: Documenting and tracking issues in a RAID log ensures they're addressed promptly. Timely resolution can prevent these issues from escalating and affecting the overall project negatively.
- Better Resource Allocation: Understanding dependencies helps in optimal scheduling and sequencing of tasks, ensuring that resources (time, people, or equipment) are utilized efficiently.
- Enhanced Communication: A RAID log serves as a central communication tool. Regularly updating and reviewing it ensures that stakeholders are kept informed about potential challenges, progress, and decisions.
- Improved Decision-Making: With a clear view of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies, it’s easier for managers to make better decisions that align with the project's objectives and constraints.
- Accountability: Assigning responsibility for each item in the RAID log ensures accountability. “By assigning responsibility for each RAID element, you can help create a culture of accountability throughout the project lifecycle,” says Aird.
Disadvantages of RAID Analysis in Project Management
RAID analysis in project management can introduce challenges such as overcomplexity for smaller projects, time consumption, and false security. Additionally, the process might be seen as bureaucratic red tape, making it difficult to secure stakeholder buy-in.
Here are some disadvantages of using RAID analysis in project management:
- Overcomplexity: For smaller projects, the RAID process might seem overly extensive or cumbersome, leading to overanalysis.
- Time Consumption: “Conducting a thorough RAID analysis can be time-intensive, particularly for larger projects,” says Aird. This is especially true if RAID analysis is not integrated seamlessly into the project management process.
- False Security: Relying heavily on the RAID log might give stakeholders a false sense of security, assuming all potential issues are already captured when unexpected challenges can still arise.
- Resource Intensity: Proper maintenance of a RAID log requires dedicated resources, which might strain smaller teams or budgets. “RAID elements can change, so the analysis is never done,” explains Aird. “It requires ongoing maintenance, which can be resource-intensive if not managed effectively.”
- Outdated Data: If the RAID log is not updated regularly, it can quickly become outdated, making it less effective and potentially misleading. Some organizations might find it easier to use an issue tracking template to track items that need attention during a project.
- Identification Bias: There is a possibility of focusing on familiar or recent risks and issues, overlooking less obvious but equally important ones.
- Perception as Bureaucracy: Some stakeholders might view the RAID process as mere red tape, leading to resistance or lack of support.
When to Use RAID Analysis in Project Management
RAID logs are great for overcoming obstacles, but can be overly complex or time-consuming. Use them for projects that require detailed oversight. They are also good for identifying potential risks and issues that can significantly impact project outcomes.
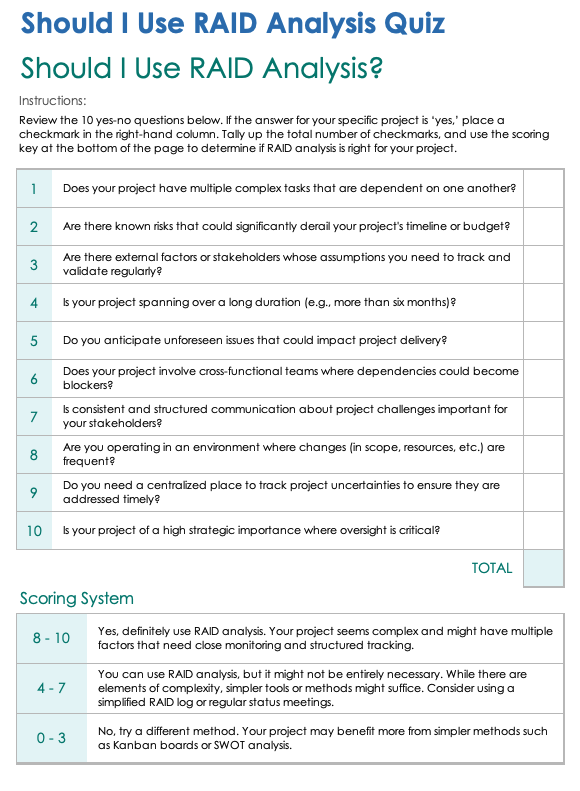
Should I Use RAID Analysis Quiz
Download the Should I Use RAID Analysis Quiz for Microsoft Word
To use this handy, printable checklist, review each yes-no question and enter a checkmark or other symbol in the column when the answer is “yes.” When done, tally your score to determine whether or not RAID analysis is right for your current or upcoming project. These questions are designed to help project managers weigh the advantages and disadvantages of RAID analysis for a specific project.
Master Project Management With RAID Analysis from Smartsheet
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.